BIM for Building Management
Building Information Modeling (BIM) is a technology that has been used in the construction industry for years. In many projects, 3D models with properties linked to them are the basis for planning and execution. But BIM models also bring great benefit in the operational phase and can serve as the basis for efficient building management.
What is Building Information Modeling (BIM)?
Building Information Modeling (BIM) is a digital representation of the physical and functional characteristics of a building. It involves creating and managing information throughout the lifecycle of a building project, from design and construction to operation and maintenance. BIM enables collaboration among architects, engineers, contractors, and other stakeholders by providing a shared, detailed 3D model that integrates various aspects of the building process. This technology enhances efficiency, reduces errors, and supports better decision-making, ultimately leading to improved project outcomes.
How does BIM work?
1. Data Collection: The process begins with gathering detailed information about the building, including architectural designs, structural details, and MEP (mechanical, electrical, and plumbing) systems.
2. 3D Modeling: Using specialized BIM software, this data is used to create a detailed 3D model of the building. This model includes all components and systems, providing a holistic view of the project.
3. Collaboration: BIM enables collaboration among various stakeholders, such as architects, engineers, and contractors, by providing a shared platform where everyone can access and update the model in real-time.
4. Simulation and Analysis: The BIM model can be used to simulate different scenarios, such as energy performance, structural integrity, and construction sequencing. This helps identify potential issues and optimize the design before construction begins.
5. Lifecycle Management: BIM continues to be useful throughout the building's lifecycle, from construction to operation and maintenance. It provides a valuable reference for facility management, renovations, and future upgrades.
BIM types
-
This approach uses a single software platform for managing and exchanging data. All project participants work within the same proprietary system, which can reduce errors and streamline workflows but may limit compatibility with other software.
-
This method promotes interoperability by using open standards and file formats, such as IFC (Industry Foundation Classes). It allows different software platforms to share data, facilitating collaboration among various stakeholders.
-
This term refers to the use of BIM within a single organization or discipline, often using one software tool. It focuses on improving internal processes and efficiencies without extensive collaboration with external parties.
-
This concept involves the comprehensive use of BIM across multiple disciplines and throughout the entire lifecycle of a building project. It emphasizes collaboration and data sharing among all stakeholders, from design and construction to operation and maintenance.

Benefits of BIM for Building Management
-
BIM facilitates better communication and collaboration among stakeholders by providing a shared, detailed 3D model that integrates various aspects of the building process.
-
With comprehensive data and visualizations, managers can make more informed decisions regarding maintenance, renovations, and space utilization.
-
By identifying potential issues early in the design phase and optimizing maintenance schedules, BIM helps reduce costs associated with repairs and operational inefficiencies.
-
BIM streamlines workflows by providing accurate and up-to-date information, reducing the time spent on manual data entry and coordination.
-
BIM supports sustainable building practices by enabling energy performance simulations and tracking the building's environmental impact.
-
BIM provides valuable data throughout the building's lifecycle, from construction to operation and maintenance, ensuring that all relevant information is easily accessible.
How dTwin uses BIM?
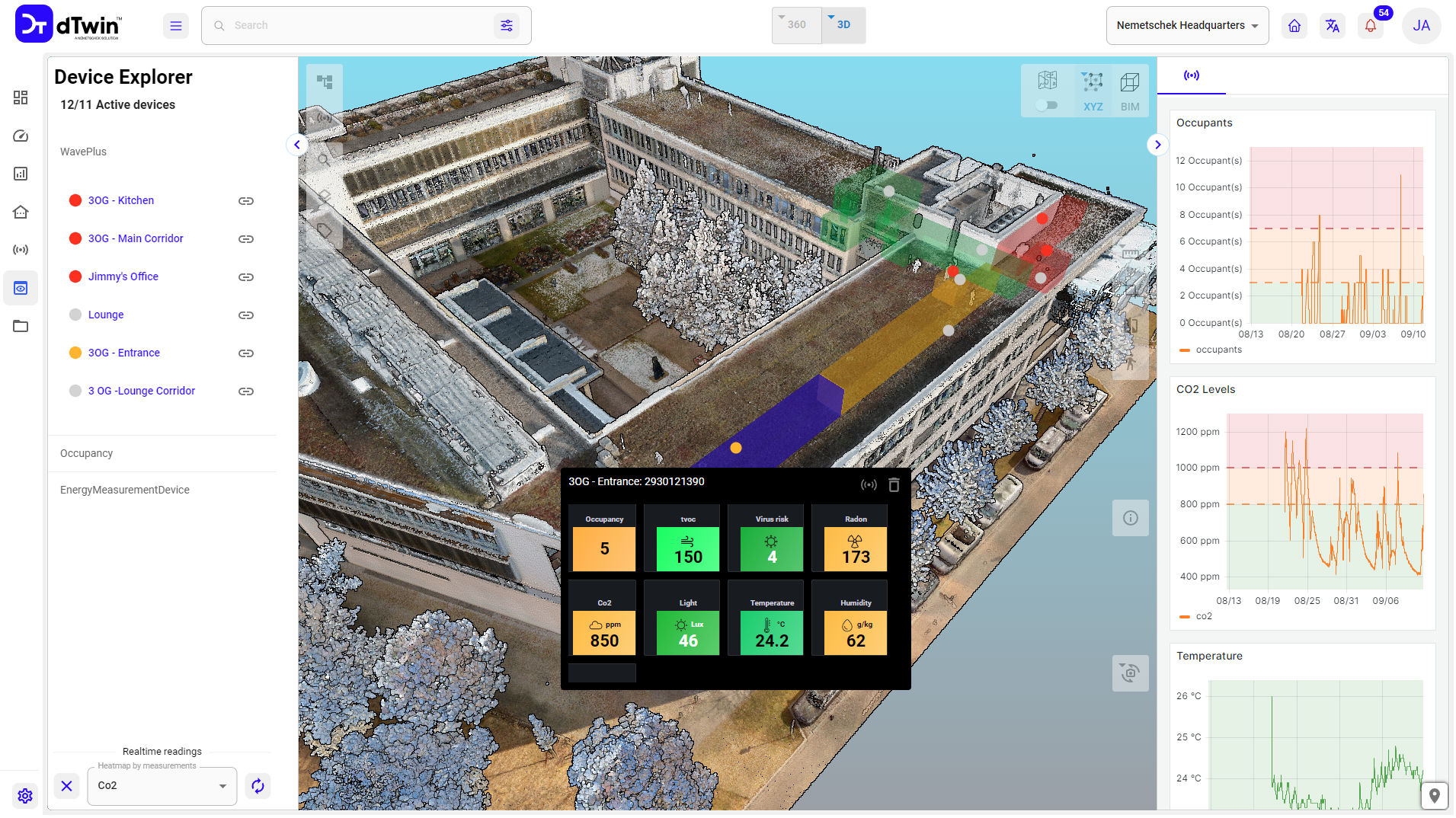
dTwin can process BIM models from a wide variety of sources. In addition to full support of IFC in various versions, native Revit files can also be imported. There is also a direct connection to BIM platforms such as Allplan Bimplus or Graphisoft BIMCloud. BCF import and export enables BIM collaboration across solutions. dTwin is therefore a real open and big BIM platform.
The BIM models can be the sole basis for visualization or can be combined with point clouds or 3D photogrammetry. The different types of visualization can be overlayed and compared. IoT sensors can be linked to the visualization resulting from laser scanning. This allows real-time data to be localized and visualized via heatmaps. But many other data such as photos, videos, descriptions or technical specifications can also be linked to the BIM models.